NASM MVP Package Example
Chapter 3 Assignments:
Expect 4-6 questions from Chapter 3
1
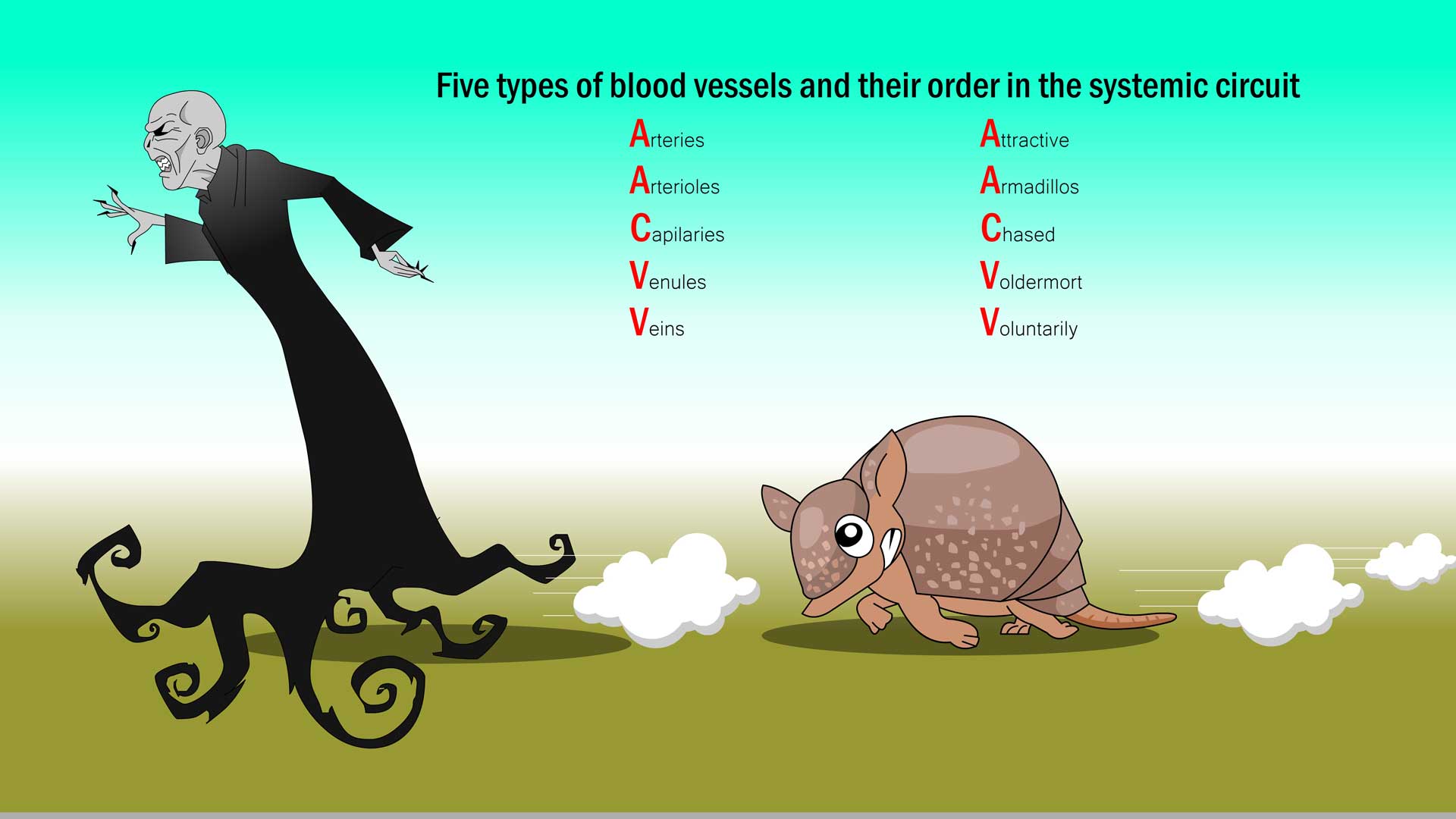
Write down the five types of blood vessels that travel through the systemic circuit and the order that the blood travels through.
2
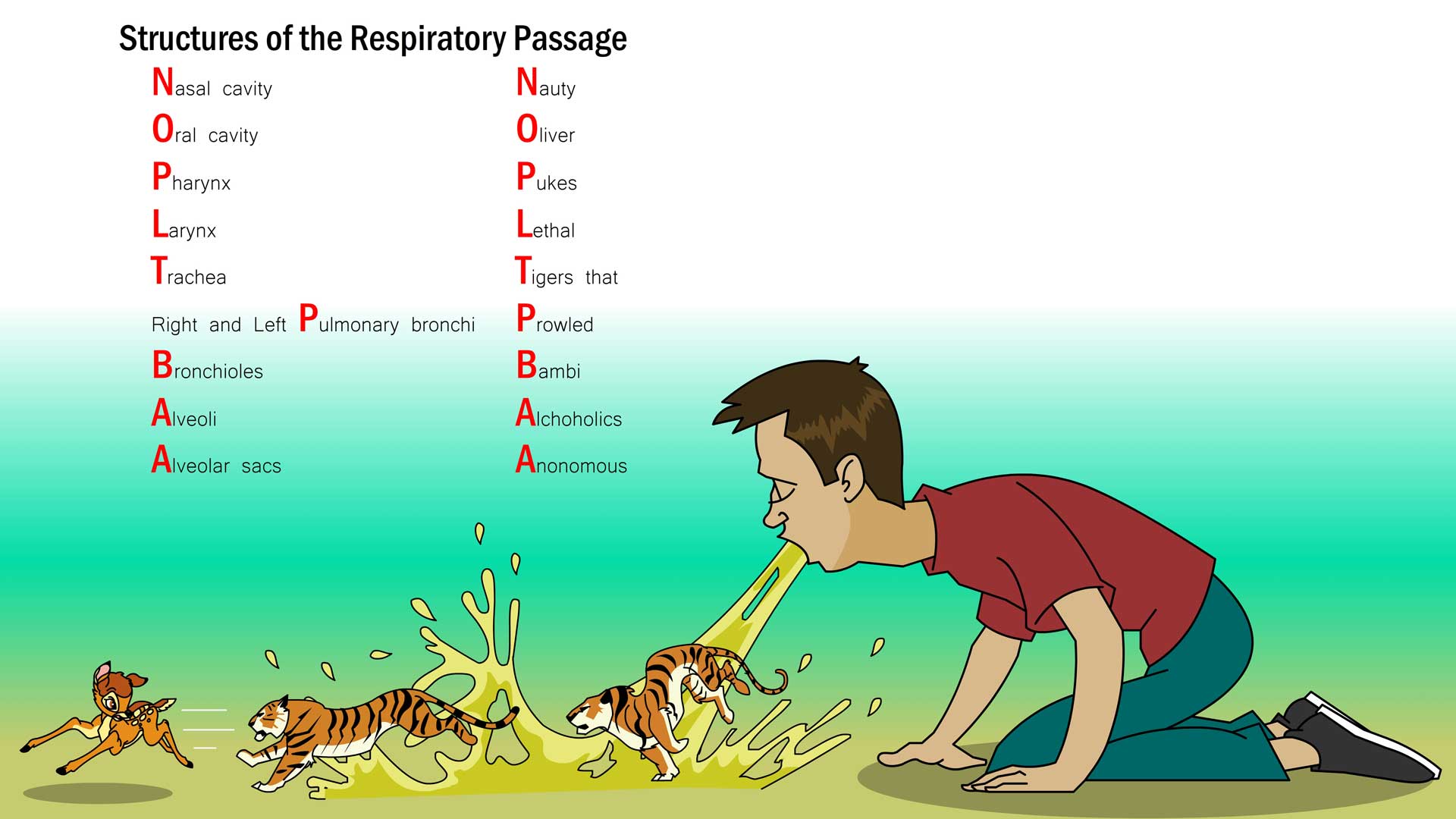
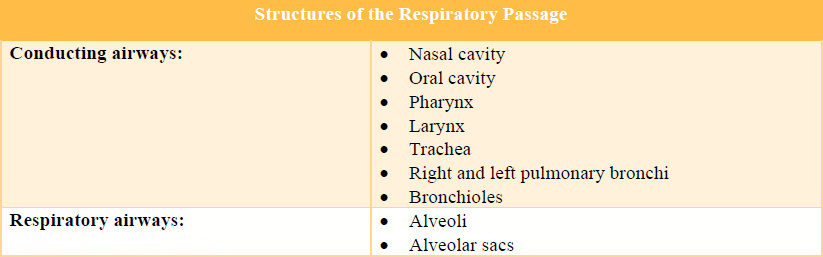
Write down the conducting and respiratory airways.
3
Discuss the structure of the heart.
4
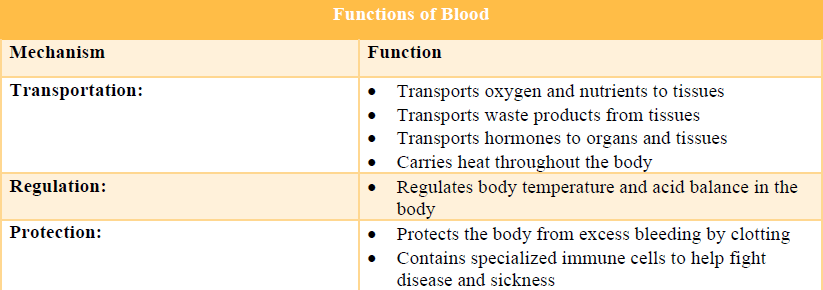
Write down and describe the three primary functions of blood from Table 3.1.
5
How can a personal trainer measure a client’s heart rate and beats per minute manually? Refer to Figure 3.4.
6
How do you measure your client’s heart rate during exercise?
7
What are the support mechanisms of Blood?
8
When is the best time to measure your client’s resting heart rate? Where is the best location to do it (on the body)? Do you press gently or hard?
9
What are the differences between cardiac output, heart rate, and stroke volume? Define all three of these.
10
What are the two forms of inspiratory ventilation?
11
What are the forms of expiratory ventilation?
12
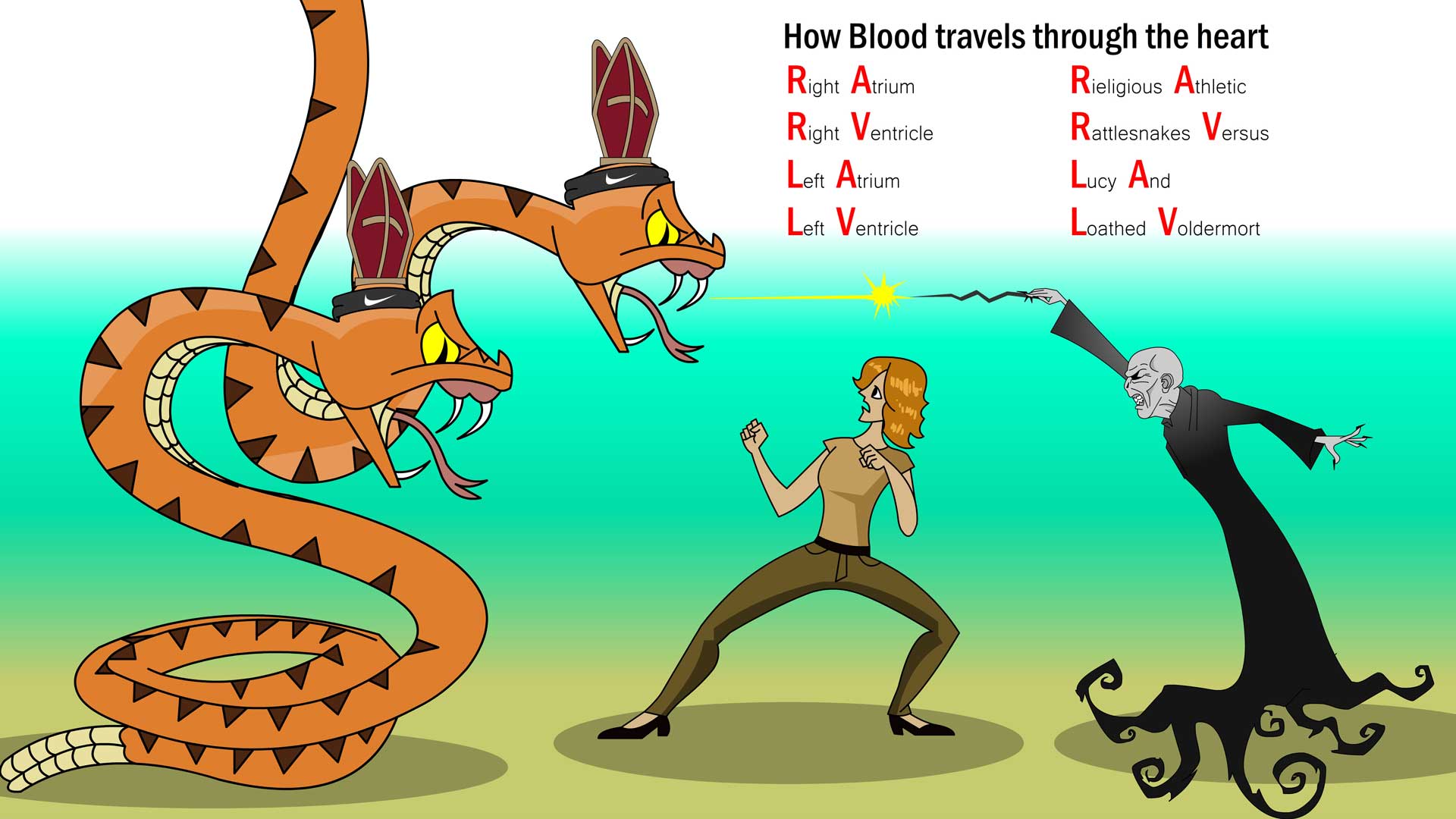
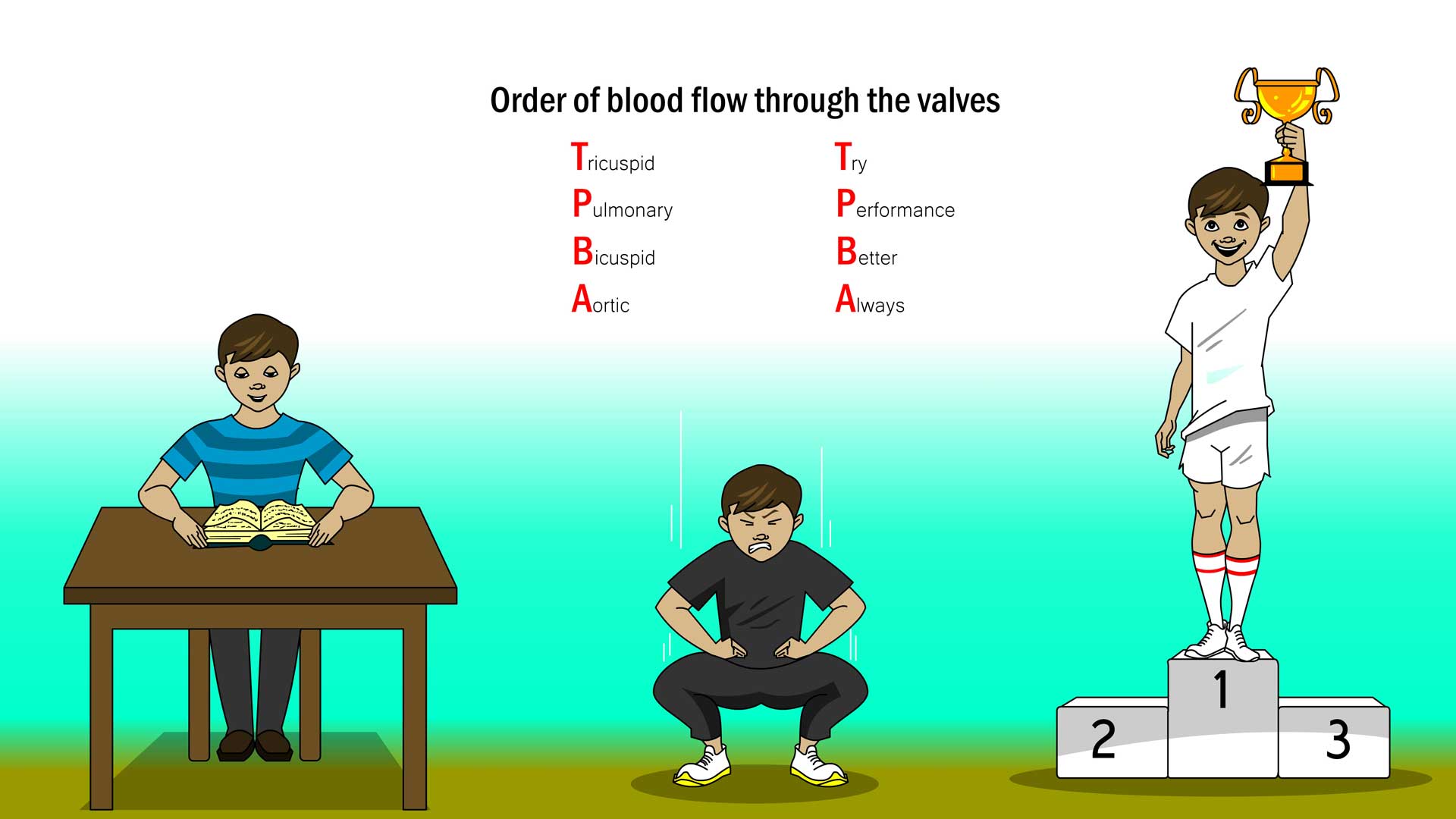
How does blood flow through the heart? Describe it in detail and draw it out to help memorize it. Go to Table 3.5 for a reference.
We include only the most important questions so that the huge NASM textbook does not completely overwhelm you.
Chapter 3 Assignment Answers:
The five types of blood vessels that travel through the systemic circuit:
⦁ Arteries: Vessels that transport blood away from the heart.
⦁ Arterioles: Small terminal branches of an artery.
⦁ Capillaries: The smallest blood vessels. This is where the oxygen exchange occurs between blood and tissues.
⦁ Venules: Very small veins that connect the capillaries to the larger veins.
⦁ Veins: The vessels that transport the un-oxygenated blood from the capillaries to the heart.
The conducting and respiratory airways:
The heart is made up of four hollow chambers with two separate pumps on each side that are interdependent. The pumps are separated by the interatrial septum and the interventricular septum. Each side has an atrium and a ventricle. Refer to the definition section for specifics on the atria and ventricles.
Transportation, regulation, and protection:
A personal trainer can calculate the heart rate manually by using the index and middle finger about 1 inch from the top of the wrist on the thumb side (radial pulse is considered more accurate). Count the number of beats in 60 seconds.
To measure your client’s heart rate during exercise, count the number of beats in six seconds and add a zero to that number. Or multiply that number by 10 to get beats per minute (BPM).
Support mechanisms of Blood
Transportation:
Transport oxygen and nutrients to issues
Transport tissue’s waste products
Transport hormones into the organs and the tissues
Carry heat in the body
Regulation
Regulate temperature, and balance acid in the body
Protection
Protect the body from excessive bleeding by using clots
Keep special immune cells to fight diseases and sicknesses
It’s best to measure your client’s resting heart rate after at least five minutes of complete rest. The best place to measure the heart rate is on the wrist (radial pulse). NASM does not recommend taking a measurement from the carotid artery. Apply light pressure as heavy pressure distorts results.
Differences between cardiac output, heart rate, and stroke volume:
Cardiac output: This is the volume of blood that is pumped by the heart per minute. Cardiac output is a function of heart rate x stroke volume.
Heart rate: The rate at which the heart beats. The average resting heart rate for an untrained adult is between 70 to 80 bpm.
Stroke volume: The amount of blood pumped out of the heart with each contraction.
The two forms of inspiratory ventilation that occur are the normal resting state breathing and the heavy breathing. We describe normal resting state breathing as quiet and this requires the use of the primary muscles of respiration. We describe heavy breathing as deep and forced, and this requires the added use of secondary respiratory muscles like the Scalenes and the Pec Minor.
Expiratory ventilation may be passive or active. In normal breathing it is passive since it is the result of relaxation of the inspiring muscles that contract. In deepened and heavy breathing, we see a reliance on the activity of expiratory muscles for the compression of the thoracic cavity to force out air.
Blood flows through the heart in four steps:
The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve.
The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle through the mitral valve.
The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve to the rest of the body.
You didn’t think we were going to leave you hanging without the answers, did you? Use these answers to double-check your own. Or, use them as a cram guide before the exam.
NASM Mnemonics
At first, mnemonics may seem like a strange way to study. But studies have shown time and time again that it is the best way to memorize information in a sequence. The goal is to make them as weird, controversial or gross as possible. Trust me, you are First Response might be “Ewwwww”, but you will never forget them. Practice what you learned in the fill in the blank section below.
Let’s practice one. How does blood travel through the heart?
Audio Study Guide
And for audio learners, we’ve got you covered as well. These are great to study while you are driving or hands-free. It is the same as the written study guide. Short and sweet. We don’t want you falling asleep from an overload of long boring lectures.
Our Intelligent flashcards: Click a card






While using our intelligent flashcards, you will rate yourself on how well you know each card from 1 (pink) to 5 (blue). Our intelligent system will start showing you you’re difficult cards frequently, and you’re easy cards only once in a while. This will save you hours of time by focusing on your weak areas. 1100 NASM flashcards in total.
Practice Exam Process
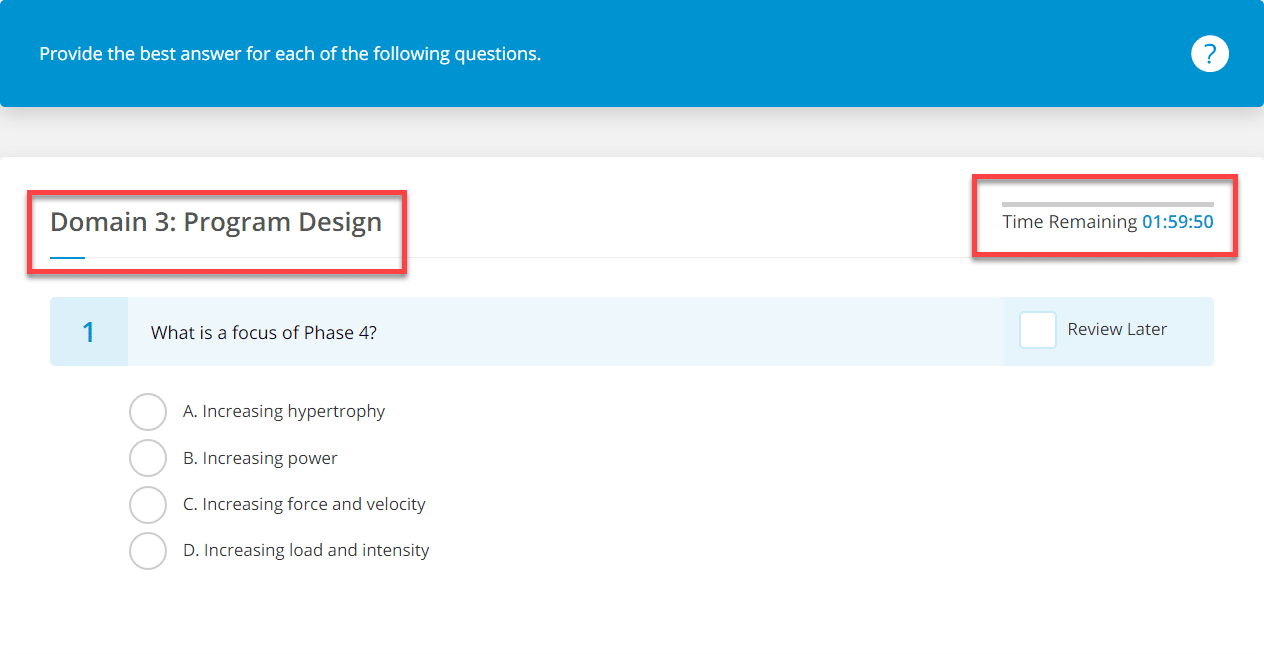
We have five full 120 question NASM practice exams. These exams have a 2-hour countdown timer to replicate what it feels like to take the real exam. You are shown which domain each question comes from.
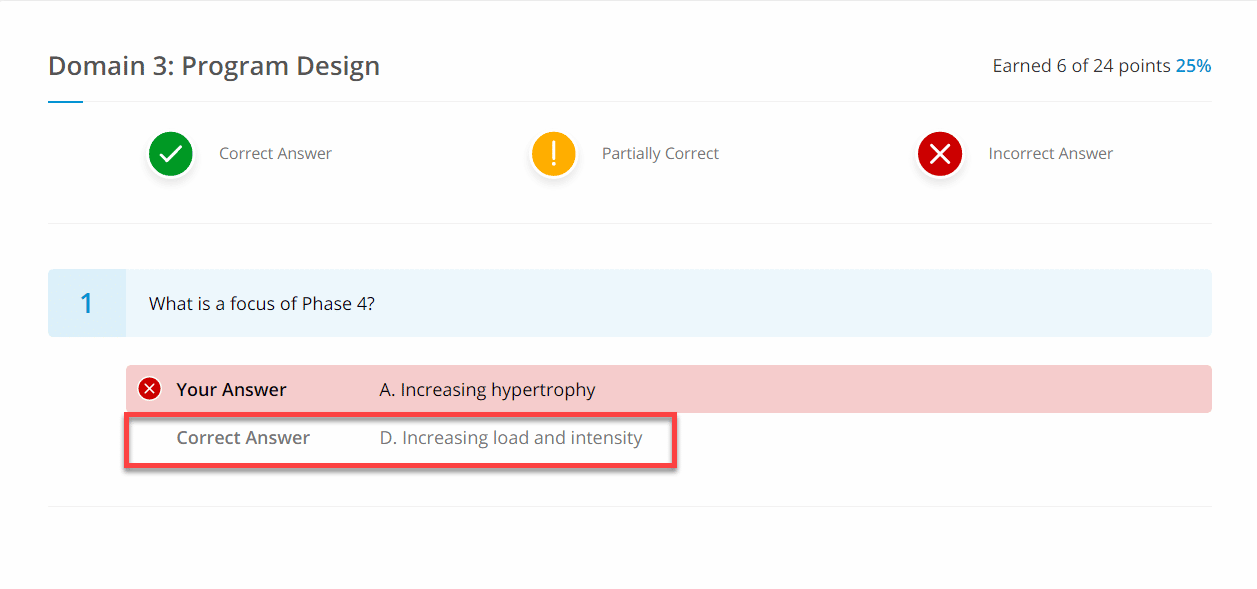
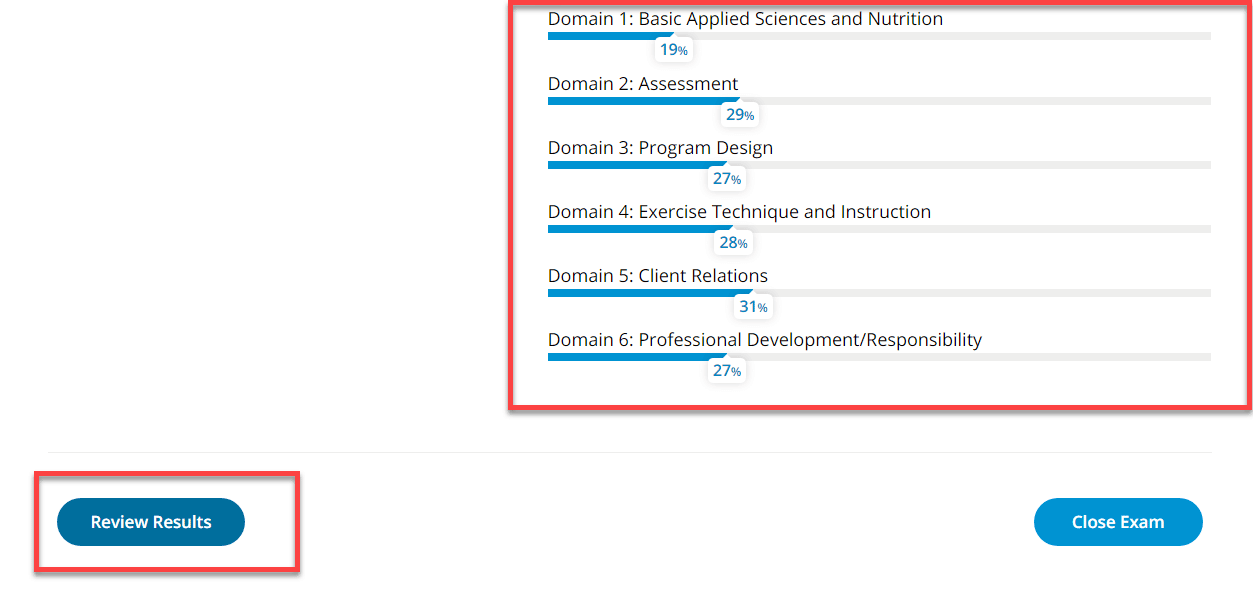
At the end of each exam you will see a breakdown of how you did in each of the six domains of study. This will help you refocus your studies on your weak areas. We have domain-specific quizzes to help you do this. Check the review results section to see the questions you got wrong.
In the “review results” section you will be able to see all the questions you got wrong as well as the correct answer
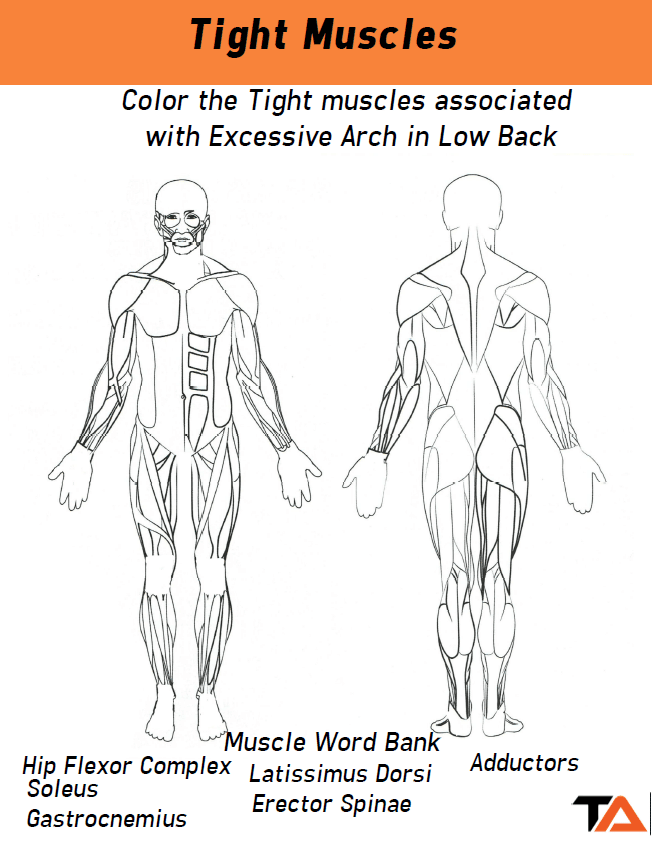
Coloring Book
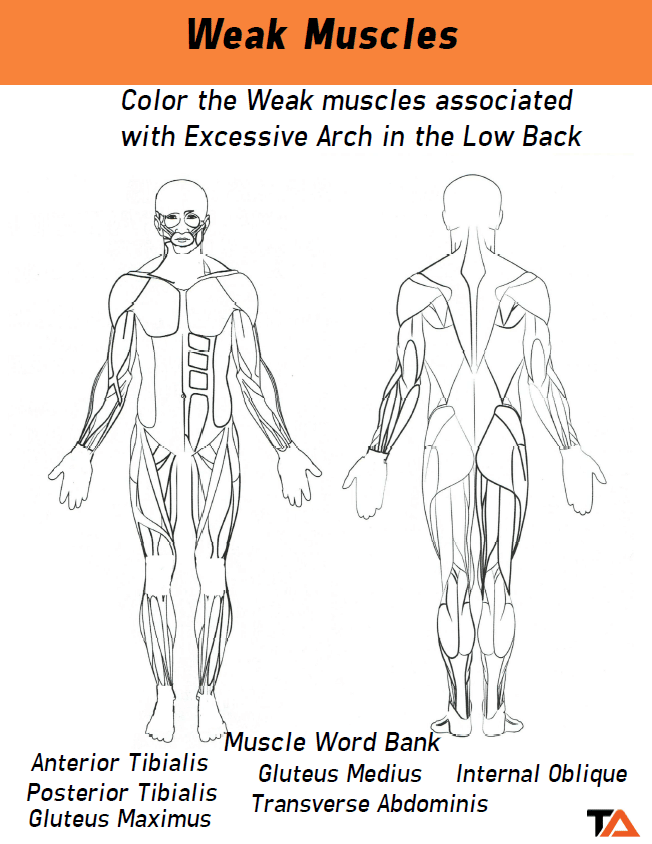
You will see up to 10 questions related to underactive and overactive muscles for specific postural assessments (Especially the overhead squat assessment) on the NASM exam. Our coloring book will be your savior for learning this section.
Additional MVP study materials and features
NASM Study Blueprint
The study blueprint contains a 16 week study plan, an 8 week plan, a 4 week plan and a 2 week plan (AKA the cram plan).
I help you decide which plan is right for you and show you exactly what to study (and how) for that time frame. This blueprint is essential if you are last second cramming and will give you the best chance to pass the exam.

NASM Cheat Sheet
The NASM cheat sheet contains the most important information that you need to focus on right before the exam.
This all fits on one sheet of paper and can be easily printed out and used the night before the test and as you are on your way to take it. This drastically helps with the last-second retention of information.

100% Exam Pass Guarantee
Our NASM MVP study package comes with an exam pass guarantee. It’s straightforward, if you somehow fail the test after using our study materials, we will refund 100% of your money. Period.
That’s how confident we are in our study materials. The retest for the NASM exam costs $199 each time! Don’t take the risk of failing.
Flash Sale: Save $100 on the NASM CPT MVP Package Today
Code: MARCHFLASH | SAVE 25%-50% on our MVP Study Programs

Questions? Use the Chatbox.